An arc on a circle measures 295 – An arc on a circle measuring 295 degrees presents a captivating enigma that invites us to explore the fascinating realm of geometry. Delving into its intricate nature, we embark on a journey to uncover the secrets it holds, unraveling the mysteries that lie within its curved embrace.
Arcs on circles possess unique characteristics and properties that distinguish them from other geometric shapes. Their measurement, closely intertwined with central angles and intercepted arcs, provides a deeper understanding of their significance. As we delve into the applications of arcs in geometry and real-world scenarios, we witness their remarkable versatility and practical relevance.
Definition of an Arc on a Circle
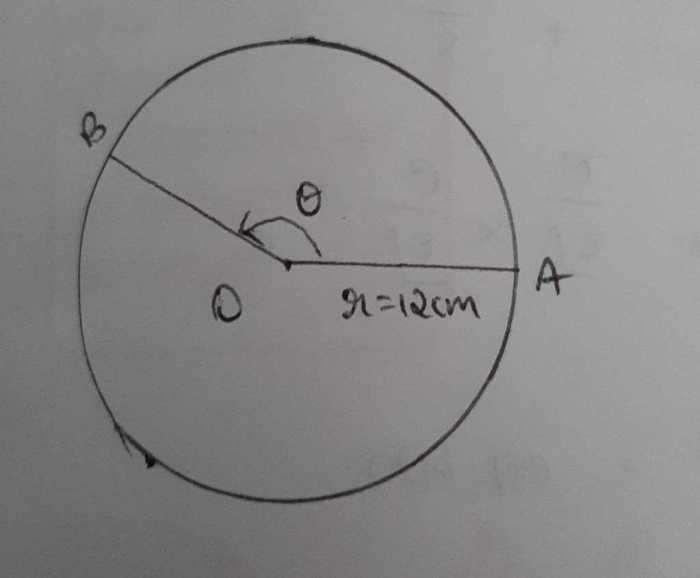
An arc on a circle is a portion of the circle’s circumference. It is defined by two endpoints on the circle and the points on the circumference between them. Arcs can be measured in degrees or radians.
Arcs have several important properties. First, the length of an arc is proportional to its central angle. This means that the larger the central angle, the longer the arc. Second, the midpoint of an arc lies on the perpendicular bisector of the chord that connects its endpoints.
Third, the area of the sector formed by an arc and its radii is proportional to the central angle.
Arcs are found in many real-world applications. For example, they are used to measure angles, to design curves, and to create patterns.
Examples of Arcs in Real-World Scenarios
- The hands of a clock move through arcs as they indicate the time.
- The path of a projectile is an arc.
- The rainbow is an arc.
Measuring an Arc
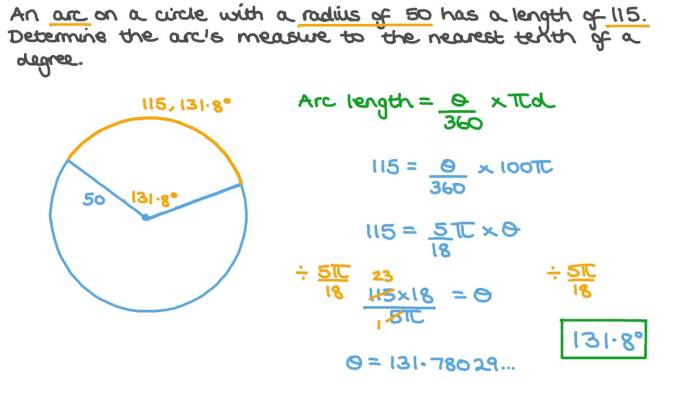
An arc is a portion of a circle’s circumference. Measuring the length of an arc is crucial in various fields, including geometry, engineering, and architecture. There are several methods for determining the length of an arc, depending on the available information.
Formula for Calculating Arc Length
The most common formula for calculating the length of an arc is:“`Arc Length = (Central Angle / 360)
2πr
“`where:* Arc Length is the length of the arc
An arc on a circle measures 295 degrees, which is a rather large portion of the circle. It’s almost like the arc of a rainbow, but a little bit more than half. In fact, it’s so large that if you were to fly a Cessna aircraft along the arc, you could almost make a complete circle.
But not quite. The arc would still be a little bit short of a full circle, but it would be pretty close. And that’s pretty impressive for an arc on a circle.
- Central Angle is the angle formed by the radii drawn from the center of the circle to the endpoints of the arc, measured in degrees
- r is the radius of the circle
Central Angle and Intercepted Arc
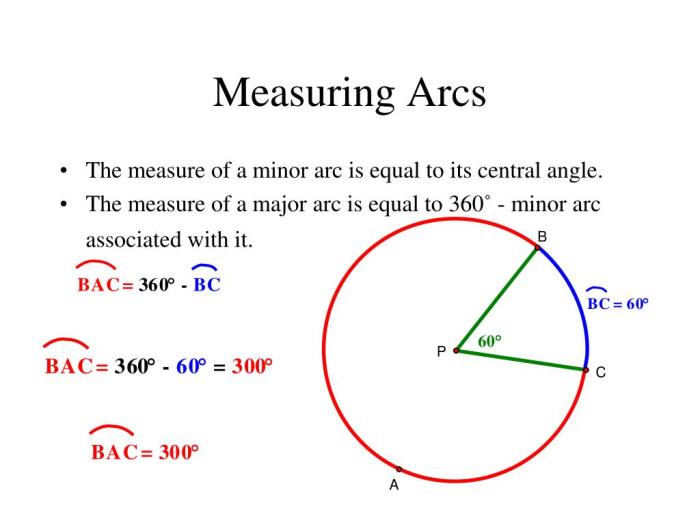
An arc on a circle is a part of the circle’s circumference. The central angle of an arc is the angle formed by two radii drawn from the center of the circle to the endpoints of the arc. The intercepted arc is the part of the circle’s circumference that lies between the endpoints of the arc.
Relationship between Central Angle and Intercepted Arc
The central angle and the intercepted arc are directly proportional. This means that as the central angle increases, the intercepted arc also increases. Conversely, as the central angle decreases, the intercepted arc also decreases.
Examples of Arcs with Different Central Angles
Here are some examples of arcs with different central angles:
- A semicircle has a central angle of 180 degrees and an intercepted arc of half the circle’s circumference.
- A quarter circle has a central angle of 90 degrees and an intercepted arc of one-quarter of the circle’s circumference.
- An arc with a central angle of 30 degrees has an intercepted arc that is one-twelfth of the circle’s circumference.
Types of Arcs: An Arc On A Circle Measures 295
Arcs can be classified into different types based on their size and shape. Each type has its own unique properties and characteristics.
Minor Arc
A minor arc is an arc that measures less than 180 degrees. It is the shorter of the two arcs that can be drawn between two points on a circle.
Major Arc
A major arc is an arc that measures more than 180 degrees. It is the longer of the two arcs that can be drawn between two points on a circle.
Semicircle
A semicircle is an arc that measures exactly 180 degrees. It is half of a circle.
Quarter Circle
A quarter circle is an arc that measures exactly 90 degrees. It is one-fourth of a circle.
Congruent Arcs
Congruent arcs are arcs that have the same measure. They may or may not be located in the same circle.
Applications of Arcs in Geometry
Arcs are widely employed in geometric constructions, serving as essential tools for solving geometric problems. They provide precise measurements and enable the creation of intricate shapes and figures.
Geometric Constructions Involving Arcs
*
-*Bisecting Angles
Arcs can be used to construct angle bisectors, which divide angles into two equal parts. By drawing an arc from the vertex of the angle, intersecting the sides at equal distances, the midpoint of the intercepted arc forms the angle bisector.
-
-*Constructing Perpendiculars
Arcs can be utilized to construct perpendicular lines to a given line segment. By drawing two arcs of equal radii from the endpoints of the line segment, the point where the arcs intersect forms the foot of the perpendicular line.
-*Creating Tangent Lines
Arcs are instrumental in constructing tangent lines to circles. By drawing an arc from the center of the circle, passing through a given point outside the circle, the tangent line is formed by the intersection of the arc with the circle.
Applications of Arcs in Real-World Scenarios
Beyond their theoretical significance, arcs find practical applications in diverse fields, ranging from engineering and architecture to design and everyday life. Understanding their uses helps us appreciate their relevance in the real world.
Engineering
Arcs are essential in engineering for designing structures that withstand various forces and stresses. For example, bridges and arches are designed using arcs to distribute weight and create stability. In mechanical engineering, arcs are used in gears and camshafts to transmit motion and power.
Architecture
Arcs play a crucial role in architecture, shaping the form and function of buildings. They are used to create aesthetically pleasing curves, such as in domes and arches, and to enhance structural integrity. For instance, the iconic dome of St.
Peter’s Basilica in Rome is constructed using multiple arcs.
Design, An arc on a circle measures 295
In design, arcs are used to create visually appealing and functional objects. They are found in product design, furniture, and even graphic design. For example, the curved edges of a smartphone or the ergonomic handle of a chair utilize arcs to enhance both aesthetics and usability.
Questions and Answers
What is the relationship between an arc and its central angle?
The central angle of an arc is the angle formed by the two radii that connect the endpoints of the arc to the center of the circle.
How do you calculate the length of an arc?
The length of an arc can be calculated using the formula: length = (central angle/360) x 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
What are the different types of arcs?
Arcs can be classified into various types based on their size and shape, such as major arcs, minor arcs, semicircles, and quarter circles.
