Cellular respiration an overview pogil answers – Unveiling the intricate world of cellular respiration, this comprehensive overview delves into the fundamental processes that power the life of all organisms. Cellular respiration, a ubiquitous biochemical pathway, serves as the primary means by which cells extract energy from nutrients, enabling them to perform essential functions and sustain life.
This exploration will unravel the intricate stages of cellular respiration, from the initial breakdown of glucose to the final synthesis of ATP, the universal energy currency of cells. Along the way, we will uncover the key enzymes and mechanisms involved, highlighting their critical roles in energy production and cellular regulation.
Cellular Respiration Overview
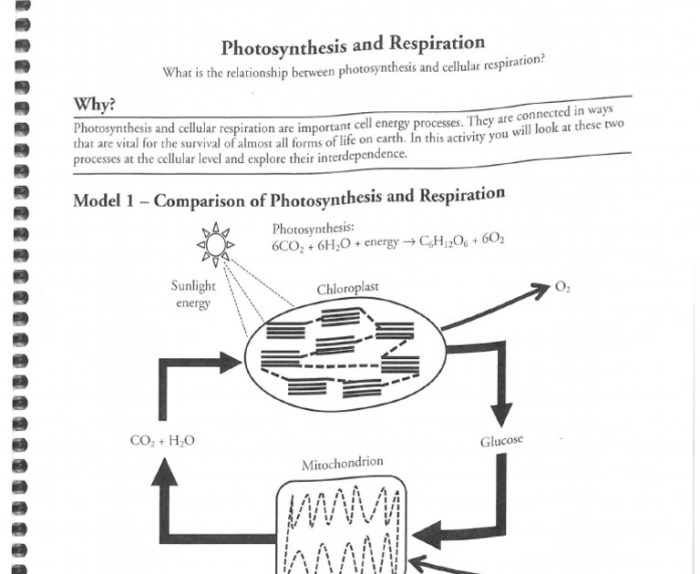
Cellular respiration is a fundamental metabolic process that converts chemical energy stored in glucose into usable energy in the form of ATP. It occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
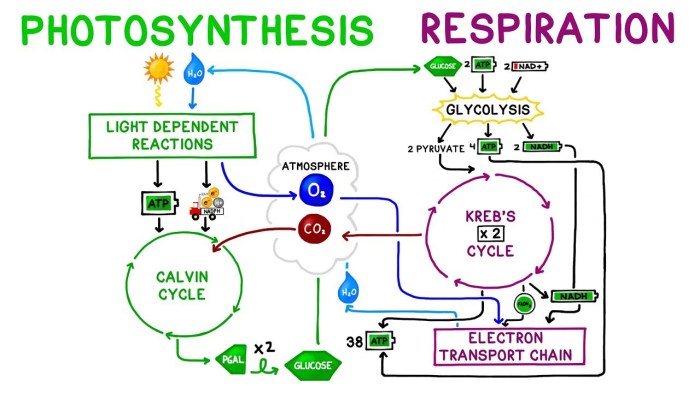
Cellular respiration involves three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation. Each stage plays a crucial role in the overall energy production process.
Cellular respiration is essential for life, providing the energy necessary for cells to carry out their functions, such as growth, reproduction, and maintenance.
Glycolysis, Cellular respiration an overview pogil answers
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm and involves the breakdown of glucose, a six-carbon sugar, into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon compound.
Glycolysis consists of ten enzymatic reactions, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme. The net energy yield of glycolysis is two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH, a high-energy electron carrier.
Glycolysis is regulated by several factors, including the availability of glucose, ATP, and NAD+.
Pyruvate Oxidation and the Citric Acid Cycle
Pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle occur in the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA, which then enters the citric acid cycle.
The citric acid cycle consists of nine enzymatic reactions, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme. The net energy yield of the citric acid cycle is three molecules of NADH, one molecule of FADH2, and one molecule of ATP.
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation
The electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation occur in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes that pass electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which the energy released from the electron transport chain is used to pump protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient. The proton gradient drives the synthesis of ATP by ATP synthase.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the most efficient stage of cellular respiration, generating the majority of the ATP produced.
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen. It is less efficient than aerobic respiration, producing only two molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose.
There are two main types of anaerobic respiration: lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation.
Anaerobic respiration is used by many organisms, including bacteria, yeast, and muscle cells, when oxygen is not available.
Regulation of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is regulated by several factors, including the availability of oxygen, ATP, and NAD+.
The rate of cellular respiration is also coordinated with other metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
Hormones, such as insulin and glucagon, play a role in regulating cellular respiration.
Questions Often Asked: Cellular Respiration An Overview Pogil Answers
What is the primary function of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration’s primary function is to generate ATP, the energy currency of cells, through the breakdown of nutrients.
What are the three main stages of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and the electron transport chain (oxidative phosphorylation) constitute the three primary stages of cellular respiration.
Where does cellular respiration occur within the cell?
Cellular respiration primarily takes place within the mitochondria, specialized organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.