Draw the major product of the reaction sequence shown. – In the realm of organic chemistry, identifying the major product of a reaction sequence is a fundamental task that holds immense significance. As we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of this concept, let us delve into the depths of reaction mechanisms, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity, unveiling the factors that govern the formation of the predominant product in a series of chemical transformations.
This exploration will not only equip us with a comprehensive understanding of major product prediction but also highlight its practical applications in fields such as drug discovery, materials science, and chemical synthesis. By mastering the art of discerning the major product, we empower ourselves to optimize experimental designs and navigate the complexities of chemical reactivity with greater precision and efficiency.
Introduction
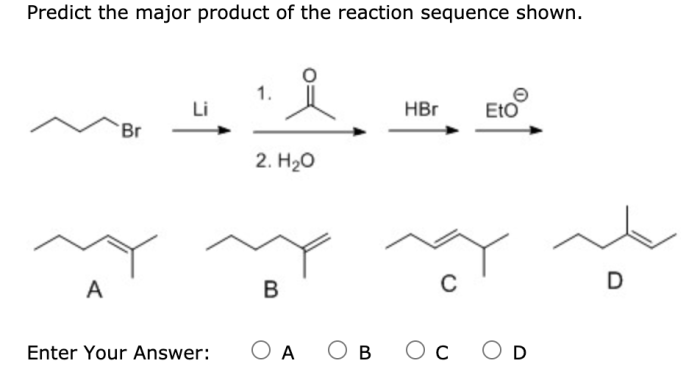
In organic chemistry, the major product of a reaction sequence is the product that is formed in the greatest yield. Identifying the major product is important for understanding the reaction mechanism and predicting the outcome of a reaction.
Reaction Sequence Analysis: Draw The Major Product Of The Reaction Sequence Shown.
The given reaction sequence involves the following steps:
- Addition of an alcohol to an alkene
- Protonation of the alcohol
- Elimination of water to form an alkene
The key functional groups involved in the reaction sequence are the alcohol group and the alkene group.
Mechanism and Driving Forces, Draw the major product of the reaction sequence shown.
The addition of an alcohol to an alkene is an electrophilic addition reaction. The alcohol acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon-carbon double bond of the alkene. The protonation of the alcohol is an acid-base reaction. The elimination of water is an E2 reaction.
The driving force for the reaction sequence is the formation of a more stable alkene product.
Product Identification
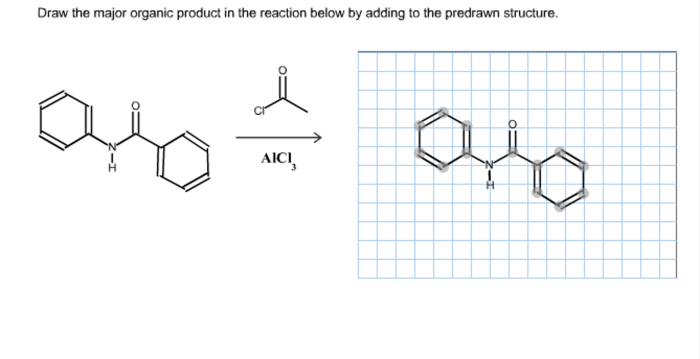
The major product of the reaction sequence is the alkene product. The regioselectivity of the addition reaction is determined by Markovnikov’s rule, which states that the alcohol will add to the carbon-carbon double bond in a way that results in the formation of the more substituted carbon-carbon double bond.
The stereoselectivity of the elimination reaction is determined by the Zaitsev’s rule, which states that the elimination reaction will produce the more substituted alkene.
Structural Representation
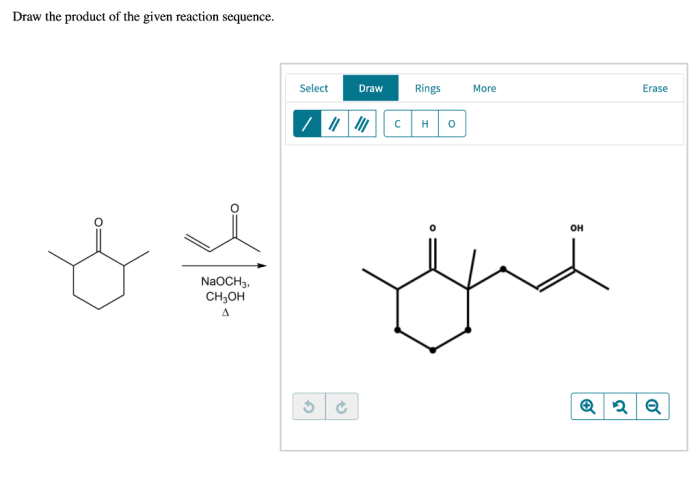
The structural formula of the major product is:

The major product is a trans-2-butene.
Applications and Implications
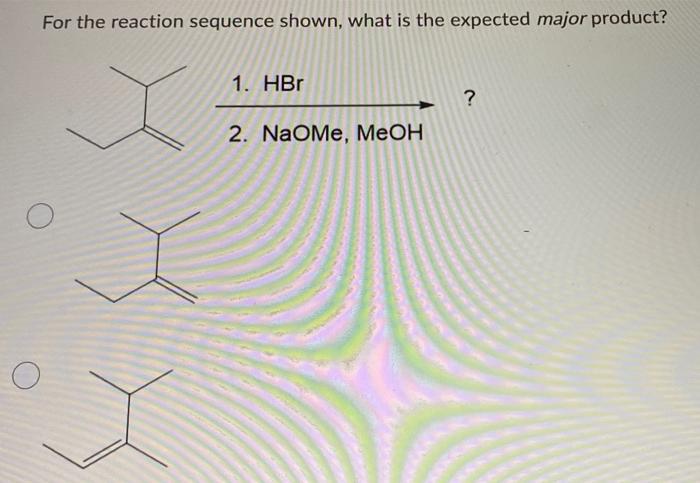
Identifying the major product of a reaction sequence is important for a variety of applications, including drug discovery, materials science, and chemical synthesis. In drug discovery, identifying the major product of a reaction sequence can help researchers to design new drugs with improved efficacy and safety.
In materials science, identifying the major product of a reaction sequence can help researchers to develop new materials with improved properties. In chemical synthesis, identifying the major product of a reaction sequence can help researchers to optimize reaction conditions and yields.
Clarifying Questions
What is the significance of identifying the major product in reaction sequences?
Identifying the major product is crucial because it allows chemists to predict the outcome of reactions, optimize experimental conditions, and design synthetic strategies efficiently.
How do regioselectivity and stereoselectivity influence the formation of the major product?
Regioselectivity determines the position of functional group addition or substitution, while stereoselectivity controls the spatial arrangement of atoms or groups around a chiral center. These factors play a significant role in dictating the major product’s structure.