Activity-based costing treats organization-sustaining costs as – With activity-based costing (ABC) treating organization-sustaining costs as indirect costs, organizations gain a granular understanding of their cost structure, leading to more accurate decision-making and improved profitability.
ABC recognizes that organization-sustaining costs, such as rent, utilities, and salaries, are necessary for the overall functioning of the organization but are not directly attributable to specific products or services. By allocating these costs based on the activities that consume them, ABC provides a more accurate picture of the true cost of each offering.
Activity-Based Costing Fundamentals

Activity-based costing (ABC) is a costing method that assigns costs to activities and then to products or services based on the activities that are performed to produce them. This method provides a more accurate view of the costs of products and services than traditional costing methods, which simply allocate costs based on direct labor hours or machine hours.
ABC is based on the following core principles:
- Activities are the fundamental unit of cost.
- Activities consume resources.
- Activities drive costs.
ABC has several advantages over traditional costing methods, including:
- Improved accuracy of cost information
- Better decision-making about products, services, and processes
- Reduced costs
ABC has been successfully implemented in a variety of organizations, including:
- General Electric
- Boeing
- Ford Motor Company
Treating Organization-Sustaining Costs: Activity-based Costing Treats Organization-sustaining Costs As
Organization-sustaining costs are costs that are not directly related to the production of any particular product or service. These costs include things like rent, utilities, and salaries for administrative staff. In ABC, organization-sustaining costs are treated as indirect costs and are allocated to activities based on their consumption of resources.
For example, rent might be allocated to activities based on the amount of space that each activity uses. Utilities might be allocated to activities based on the amount of energy that each activity consumes. And salaries for administrative staff might be allocated to activities based on the amount of time that each activity requires administrative support.
By allocating organization-sustaining costs to activities, ABC provides a more accurate view of the costs of products and services. This information can then be used to make better decisions about pricing, product mix, and process improvement.
Impact on Decision-Making

ABC can improve the accuracy of cost information by providing a more detailed understanding of the costs of activities and products. This information can then be used to make better decisions about:
- Pricing: ABC can help organizations set prices that are more reflective of the true costs of their products and services.
- Product mix: ABC can help organizations determine which products and services are most profitable and which ones should be discontinued.
- Process improvement: ABC can help organizations identify areas where processes can be improved to reduce costs.
For example, a company that uses ABC might find that one of its products is actually losing money. This information could then be used to decide whether to discontinue the product or to find ways to reduce its costs.
Implementation Considerations
Implementing ABC can be a complex and time-consuming process. However, it can be a worthwhile investment for organizations that are looking to improve the accuracy of their cost information and make better decisions.
The following are some key steps involved in implementing ABC:
- Identify the activities that are performed in the organization.
- Assign costs to the activities.
- Develop a system for allocating costs to products and services.
- Implement the ABC system.
Organizations may face a number of challenges when implementing ABC, including:
- Collecting accurate data on activities and costs
- Developing a system for allocating costs to products and services
- Training employees on the new ABC system
Despite these challenges, ABC can be a valuable tool for organizations that are looking to improve their cost information and make better decisions.
Advanced Applications of ABC
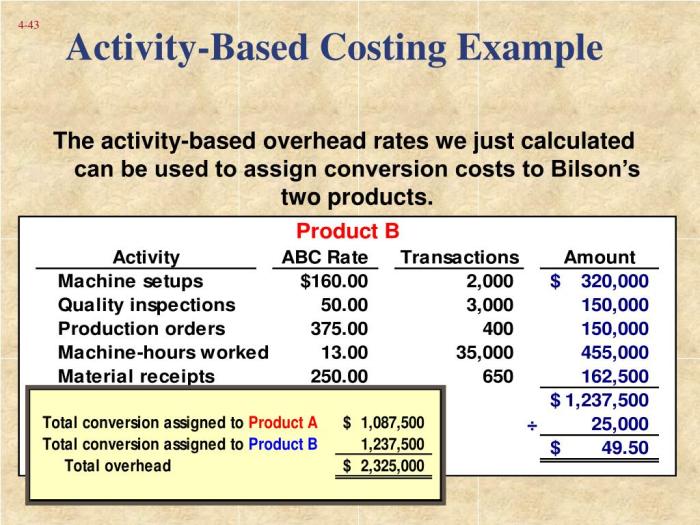
ABC can be used for a variety of advanced applications, including:
- Target costing: ABC can be used to set target costs for products and services.
- Process improvement: ABC can be used to identify areas where processes can be improved to reduce costs.
- Strategic planning: ABC can be used to support strategic planning by providing information on the costs of different products and services.
For example, a company might use ABC to set target costs for a new product. The company could then use this information to design the product and its manufacturing process in a way that meets the target costs.
FAQ Guide
What are organization-sustaining costs?
Organization-sustaining costs are indirect costs necessary for the overall functioning of an organization but not directly attributable to specific products or services.
How does ABC allocate organization-sustaining costs?
ABC allocates organization-sustaining costs based on the activities that consume them, providing a more accurate picture of the true cost of each offering.